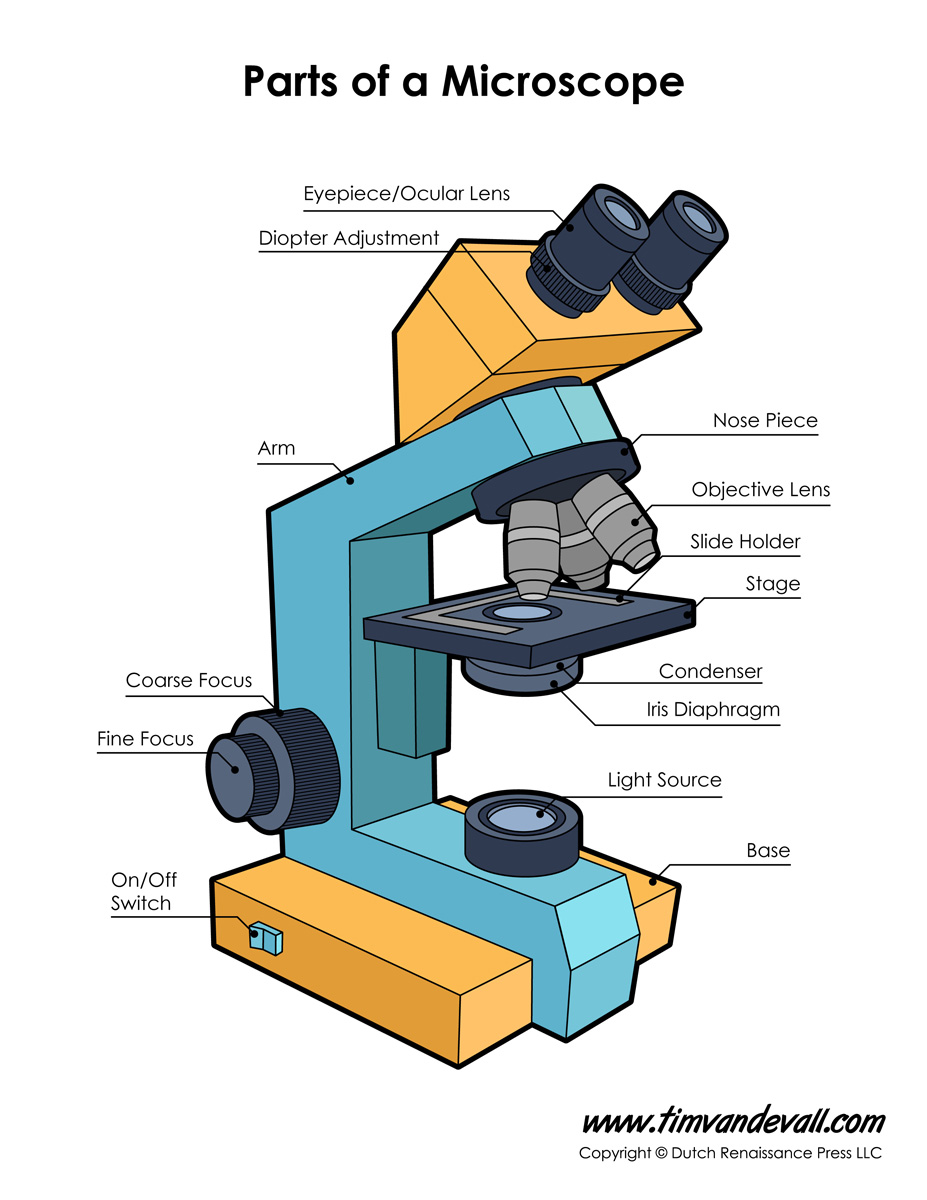
Monday September 25 Parts of a Compound Light Microscope
A labeled diagram of microscope parts furnishes comprehensive information regarding their composition and spatial arrangement within the microscope, enabling researchers to comprehend their function effectively. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the intricate parts of the microscope, exploring their functions in detail.
1.5 Microscopy Biology LibreTexts
This activity has been designed for use in homes and schools. Each microscope layout (both blank and the version with answers) are available as PDF downloads. You can view a more in-depth review of each part of the microscope here. Download the Label the Parts of the Microscope PDF printable version here.
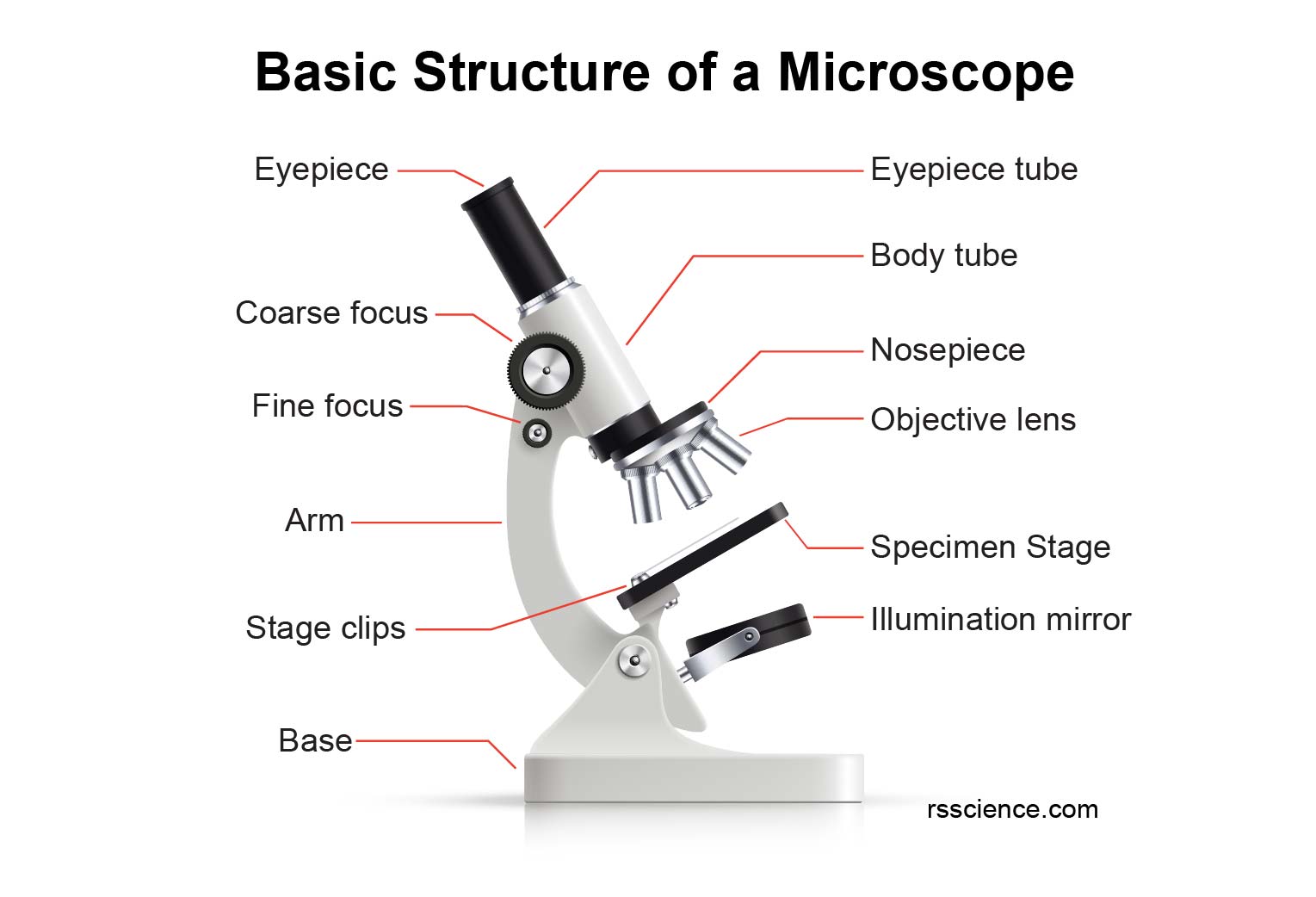
What is a Microscope? Function and Magnification Rs' Science
Mirror. The lower end of the arm or the pillar has a mirror fastened to it. On one side is a regular mirror, and on the other is a concave mirror. It is used to reflect light into the microscope for a sharper view of the specimen. A compound microscope primarily makes use of concave mirrors. Plane mirrors are occasionally also used.
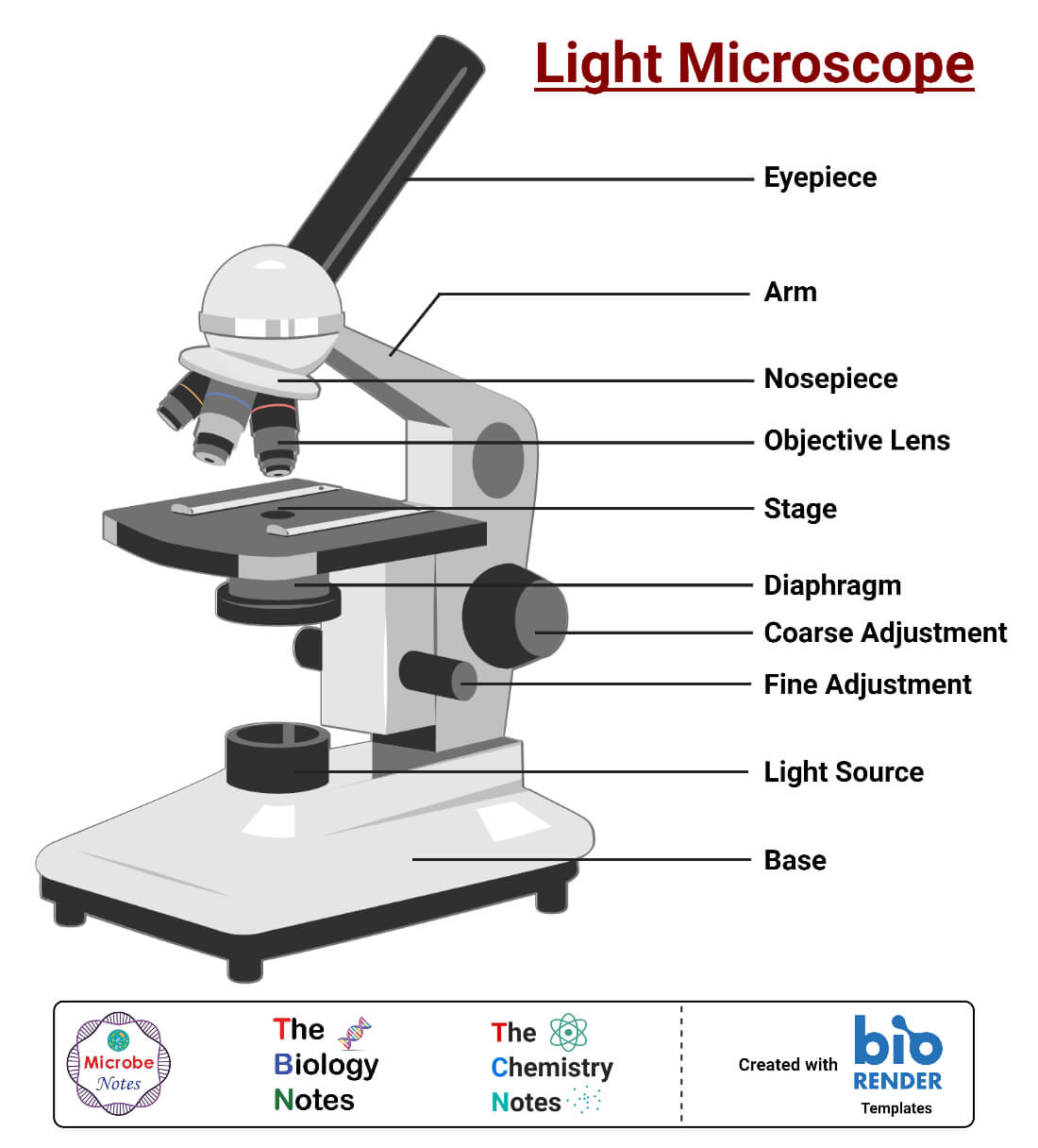
5 Types of Microscopes with Definitions, Principle, Uses, Labeled Diagrams
Table of Contents History of Microscopy: Overview What is a light microscope? Figure: Diagram of Light Microscopes, created with biorender.com Principle of a light microscope (optical microscope) Types of light microscopes (optical microscope) Brightfield Light Microscope (Compound light microscope)
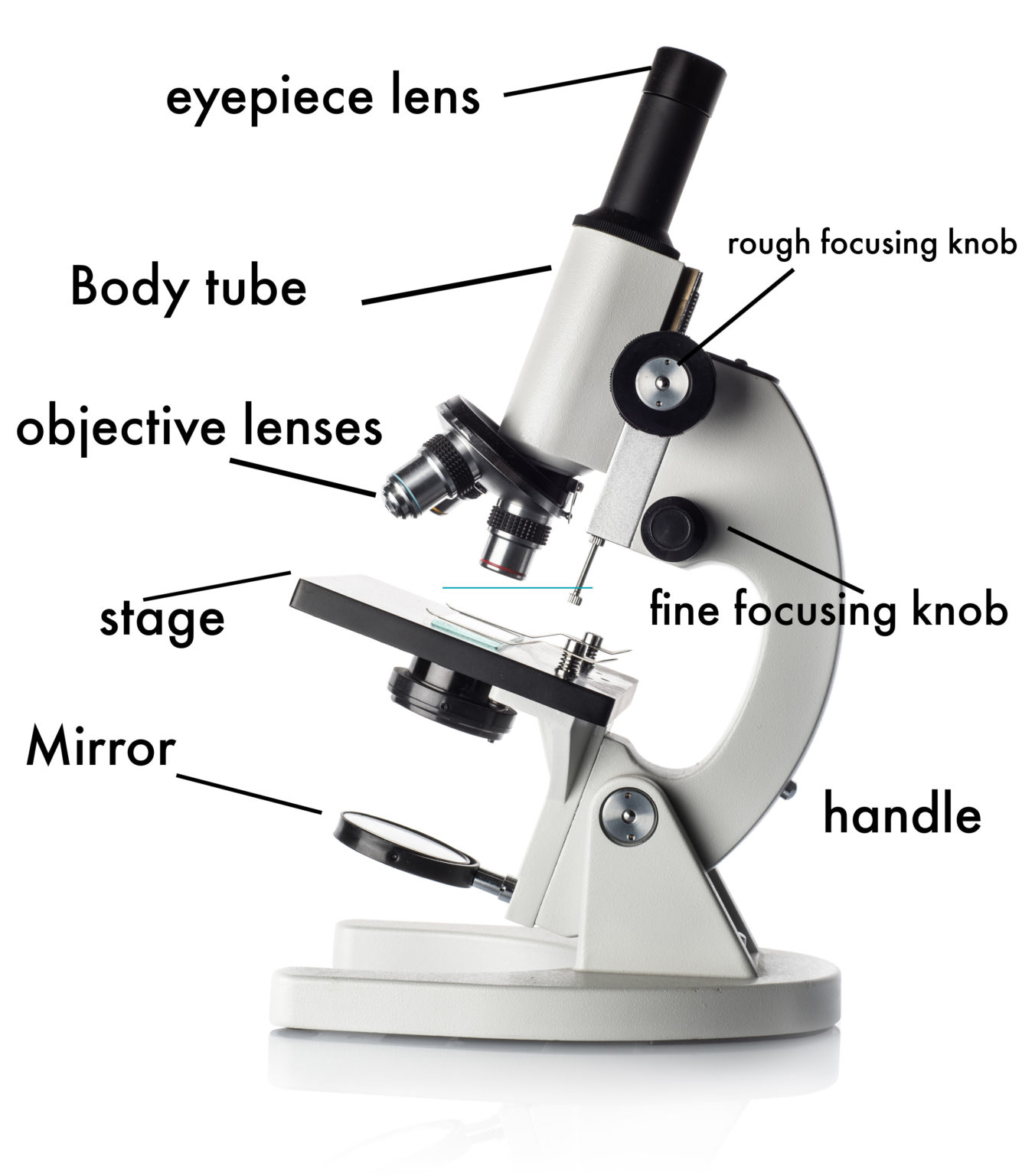
How to Use a Microscope
There are three major structural parts of a compound microscope. The head includes the upper part of the microscope, which houses the most critical optical components, and the eyepiece tube of the microscope. The base acts as the foundation of microscopes and houses the illuminator. The arm connects between the base and the head parts.
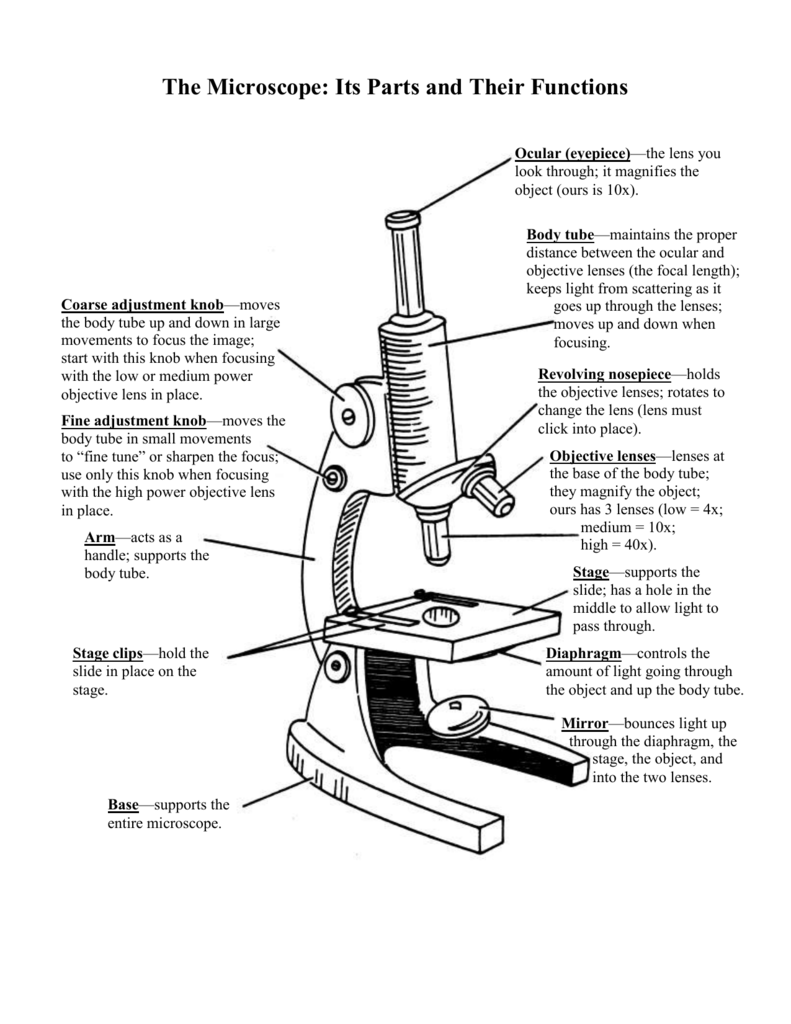
The Microscope Its Parts and Their Functions
The web page titled "Parts of a Microscope with Labeled Diagram and Functions" has the following key takeaways: 🔍 The microscope is an essential tool for scientists, researchers, and medical professionals. 🧬 The main function of a microscope is to provide a magnified view of small objects or organisms, such as bacteria, cells, or tissues.

Microscope diagram Tom Butler Technical Drawing and Illustration Projects Pinterest
Microscopy Introduction to microscopes and how they work. Covers brightfield microscopy, fluorescence microscopy, and electron microscopy. Introduction If you meet some cell biologists and get them talking about what they enjoy most in their work, you may find it comes down to one thing: secretly, they're all microscope freaks.
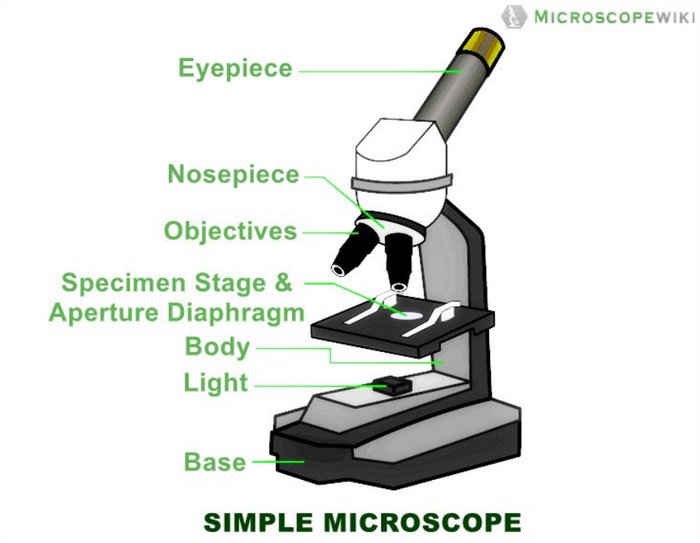
Simple Microscope Diagram (Parts labelled), Principle, Formula and Uses
Parts of the Microscope with Labeling (also Free Printouts) A microscope is one of the invaluable tools in the laboratory setting. It is used to observe things that cannot be seen by the naked eye. Table of Contents 1. Eyepiece 2. Body tube/Head 3. Turret/Nose piece 4. Objective lenses 5. Knobs (fine and coarse) 6. Stage and stage clips 7. Aperture
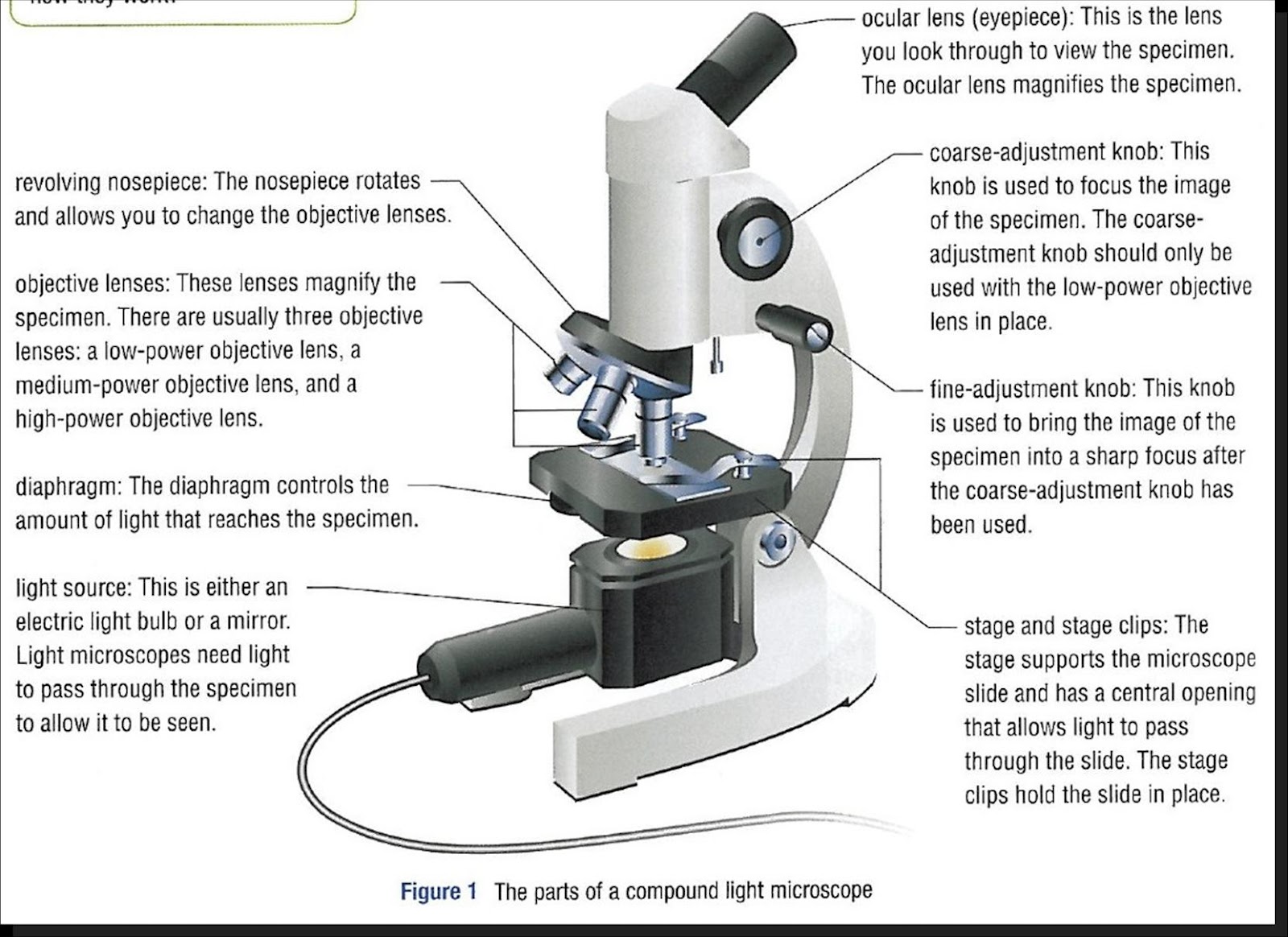
Parts Parts And Functions Of A Microscope
The microscope illustrated in Figure 5 below was manufactured by Hugh Powell and Peter Lealand around 1850. The tripod base provided a sturdy support for the microscope, which many people consider the most advanced of its period. Parts of a Powell and Leland Microscope Diagram
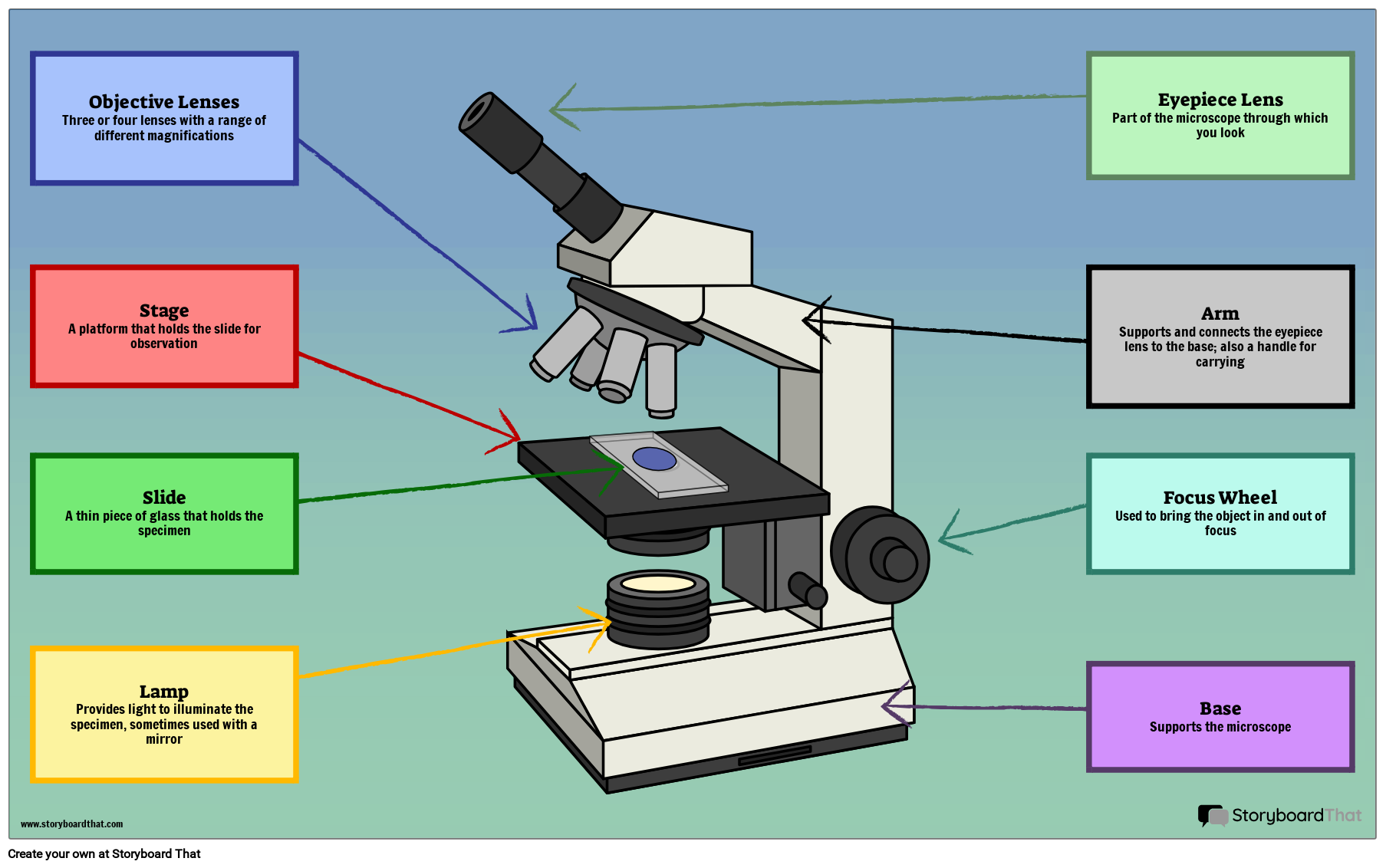
Parts of a Microscope Labeling Activity
Parts Of a microscope. The main parts of a microscope that are easy to identify include: Head: The upper part of the microscope that houses the optical elements of the unit.; Base: The base is attached to a frame (arm) that is connected to the head of the device.The base of the microscope provides stability to the device and allows the user's hands to be free to manipulate other aspects of.
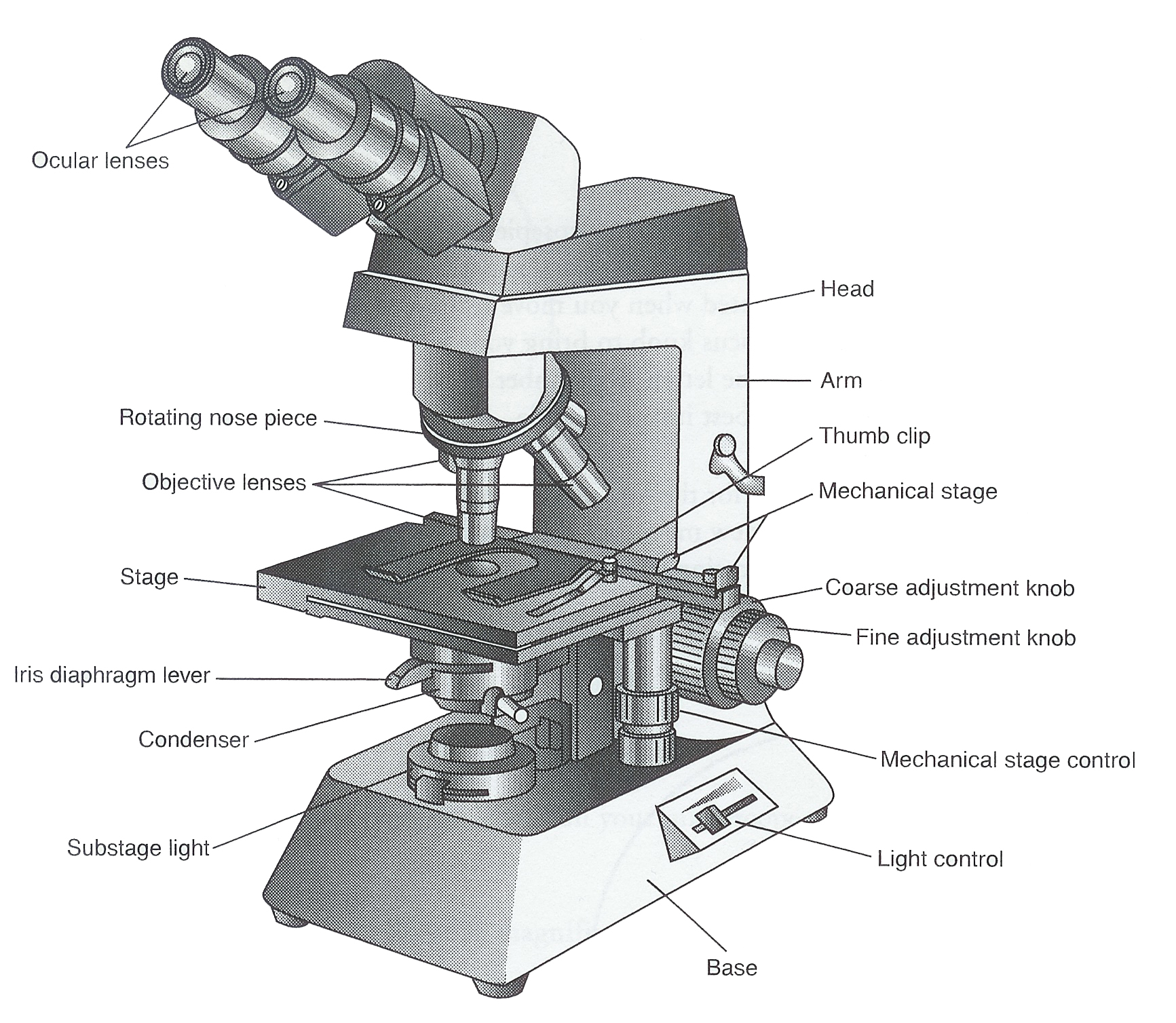
Ag Biology Unit 2
Figure: Diagram of parts of a microscope. There are three structural parts of the microscope i.e. head, arm, and base. Head - The head is a cylindrical metallic tube that holds the eyepiece lens at one end and connects to the nose piece at other end. It is also called a body tube or eyepiece tube.

301 Moved Permanently
Microscope Types (with labeled diagrams) and Functions Home / Microscope Types / Microscope - Types, Diagrams and Functions By Editorial Board October 13, 2022 Microscope - Let's split the name into two parts to understand what it actually means.
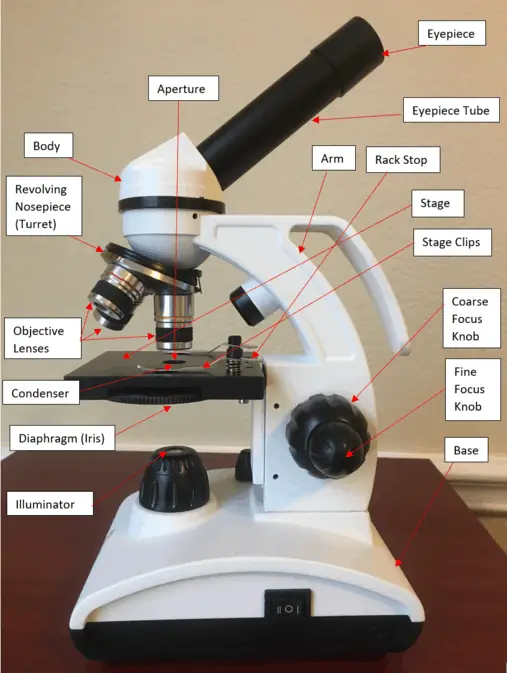
16 Parts of a Compound Microscope Diagrams and Video Microscope Clarity
1. Simple Microscope Working Principle of simple Microscope Applications of Simple Microscope Advantages of Simple Microscope Disadvantages of Simple Microscope 2. Compound Microscope Working Principle of Compound Microscope Compound Microscope Diagram Compound Microscope Parts Uses of Compound Microscope Advantages of Compound Microscope

Clipart microscope parts labeled WikiClipArt
Diaphragm (Iris) Condenser Aperture Stage Objective lens Body Tube Ocular Lens (eye-piece) Coarse and Fine Adjustment Knob Arm Base Microscope Worksheet The Light Microscope Light microscopes are used to examine cells at relatively low magnifications. Magnifications of about 2000X are the upper limit for light microscopes.
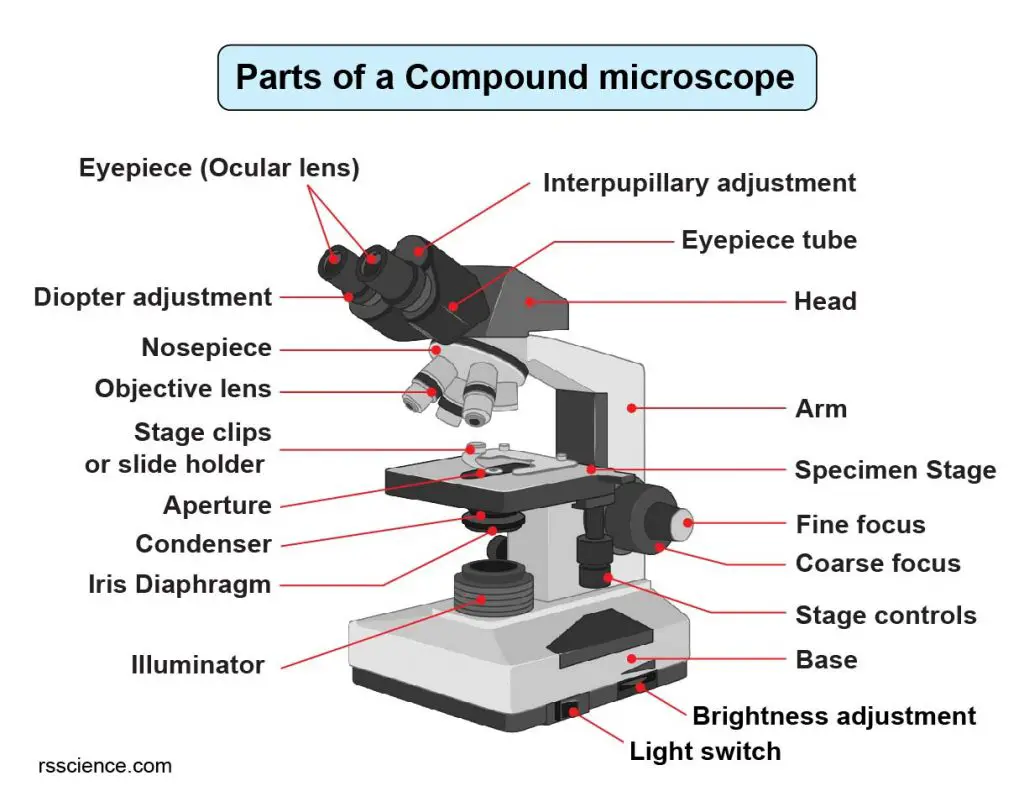
Compound Microscope Parts Labeled Diagram and their Functions Rs' Science
A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram - Science Struck A Study of the Microscope and its Functions With a Labeled Diagram To better understand the structure and function of a microscope, we need to take a look at the labeled microscope diagrams of the compound and electron microscope.

Parts of a Microscope The Comprehensive Guide Microscope and Laboratory Equipment Reviews
The hand magnifying glass can magnify about 3 to 20×. Single-lensed simple microscopes can magnify up to 300×—and are capable of revealing bacteria —while compound microscopes can magnify up to 2,000×. A simple microscope can resolve below 1 micrometre (μm; one millionth of a metre); a compound microscope can resolve down to about 0.2 μm.